How to Form the Present Continuous Tense

Let's learn the forms of the present continuous including the affirmative, negative, question and short forms. There are also lots of examples to help make everything very clear. Before we get started, please note that this is also often called the present progressive tense.
[Note: Click here to learn how to use this tense.]
Present continuous positive form
To form the present continuous, we use the am / is / are form of the verb "to be" plus the infinitive of the verb plus an -ing ending. The form is the same for each subject.
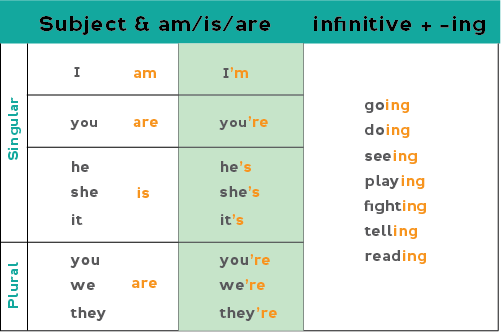
Please note as shown above that you can contract the subject and verb if you want to:
I am = I'm he is = he's she is = she's it is = it's we are = we're they are = they're
Examples:
- I am going to school. / I'm going to school.
- You are doing the dishes. You're doing the dishes.
- He's seeing his doctor now.
- She's playing with her dog outside.
- We are fighting over which tv show to watch.
- You are all telling me different stories.
- They are reading quietly before bedtime.
Present continuous negative form
To make the tense negative add "not" before the verb + -ing.
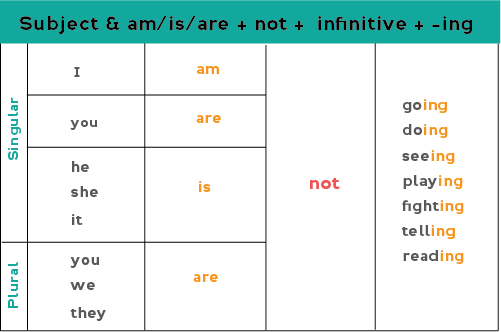
Examples:
- I am not going to bed now.
- You are not doing your homework now.
- The children are not sleeping at this time.
- My boyfriend is not telling me everything.
- They are not reading today's newspaper.
You can also use contractions with the negative form:
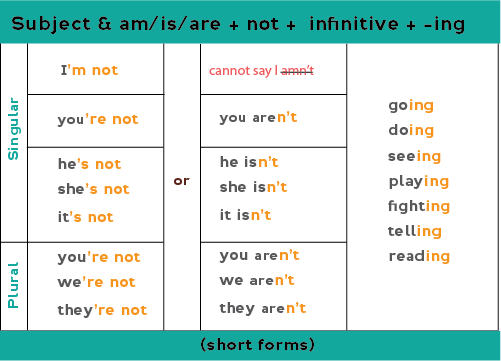
Examples:
- I'm not going to bed now. (NOT: I amn't going to bed)
- You're not doing your homework now.
- You aren't doing your homework now.
- The mouse isn't eating the cheese.
- The mouse's not eating the cheese.
- We're not buying a new car.
- We aren't buying a new car.
- They're not studying very often.
- They aren't studying very often.
Present continuous yes/no questions (positive)
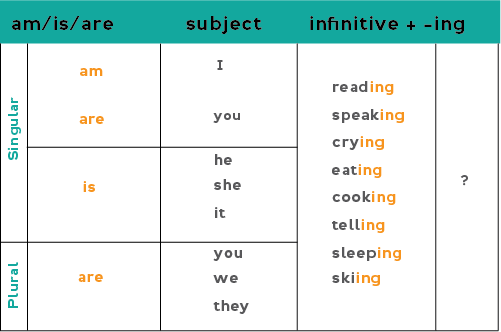
Questions that can be answered with "yes" or "no" answers are formed by inverting the subject and correct form of the verb "be" (am / is / are). (Inverting simply means we change the order of the subject and verb form:)
Affirmative statement: I am coming. (the subject "I" is first, then the verb form "am")
Affirmative question: Am I coming? (to make a question, the verb form "am" comes first then the subject "I").
Examples:
- Am I reading a book right now?
- Is he speaking on the phone with your teacher?
- Is the baby still crying?
- Is the dog eating his food now?
- Are we cooking together at this moment?
- Are they sleeping yet?
Wh- questions present continuous
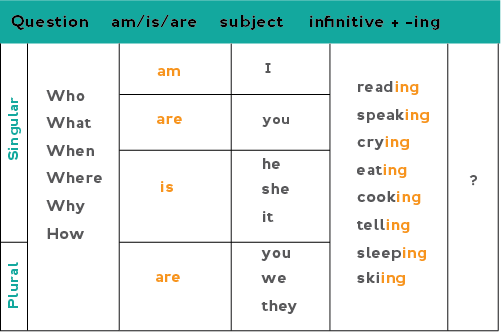
We can also use contractions for the following wh- questions:
who is = who's what is = what's where is = where's when is = when's
why is = why's how is = how's
Examples:
- Where is he going?
- Where's she traveling to?
- How are getting to the store?
- Why are the buses running late?
- What is my dog eating?
- What's the policeman saying?
- What are those kids playing with?
- Where are my children hiding?
- How's your new phone working?
Spelling changes present continuous
Be careful as there are also some spelling changes:
Spelling: Verbs that end with one -e
For verbs that end with one -e, drop the -e and add -ing. Note that these verbs the -e sound at the end is silent. (e.g., believe, bake, take, love).
- believe — believing
- bake — baking
- love — loving
- take — taking
- choke — choking
- make — making
- have — having
But:
With verbs ending with a long -e sound, add -ing as normal:
- see — seeing
- be — being
- flee — fleeing
- agree — agreeing
Spelling: Short one-syllable verbs ending in CVC
If the verb has one syllable and ends with CVC (a consonant + vowel + consonant), we double the final consonant before adding the -ing ending:
- sit — sitting
- fit — fitting
- get — getting
- plan — planning
- run — running
- put — putting
- stop — stopping
- swim — swimming
Spelling: verbs ending in w, x and y
Notice these verbs end in CVC (consonant vowel consonant). However, do not double the consonant for verbs that end in w, x or y.
- throw — throwing
- blow — blowing
- show — showing
- play — playing
- flex — flexing
Spelling: Two or more syllable verbs
When verbs ending in ending in CVC (consonant vowel consonant) have two or more syllables, double the last consonant if the last syllable is stressed.
- begin — beginning (be / GIN = the last syllable is stressed)
- control — controlling (con / TROL = the last syllable is stressed)
- forget — forgetting
- upset — upsetting
- regret — regretting
- refer — referring
- commit — committing
However, when the last syllable is not stressed, just add -ing as usual.
- benefit — benefiting ( be / NE / fit = second syllable is stressed not the last)
- happen — happening (HAPP / en = first syllable is stressed not the last)
- open — opening
- listen — listening
- deliver — delivering
Spelling: Verbs ending in -ie
If a verb ends in -ie change 'ie' to 'y' then add -ing.
- die — dying
- lie — lying
- tie — tying
Check back for exercises that will help you practice the present continuous tense in its different forms.
Now that you've learned how to form the present continuous, click here to learn how to use it.
- Home Page ›
- Main Grammar Page ›
- Use: Present Continuous >
- Form: Present Continuous
